(Ed. Note: Although I spend 2-3 hours a day reading financial newsletters, I rarely write about it on this blog because I don't want to influence readers to make fiscal decisions that they may latter regret. You've got to do your own research and make your own decisions.)
However, the following newsletter, The Subprime Debacle: Act 2 - John Mauldin's Weekly E-Letter, was so incisive that I couldn't resist passing it on. It's a free signup if you want to keep receiving it.)
There's trouble, my friends, and it is does indeed involve pool(s), but not in the pool hall. The real monster is hidden in those pools of subprime debt that have not gone away. When I first began writing and speaking about the coming subprime disaster, it was in late 2007 and early 2008. The subject was being dismissed in most polite circles. "The subprime problem," testified Ben Bernanke, "will be contained."
My early take? It would be a disaster for investors. I admit I did not see in January that it would bring down Lehman and trigger the worst banking crisis in 80 years, less than 18 months later. But it was clear that it would not be "contained." We had no idea.
I also said that it was going to create a monster legal battle down the road that would take years to develop. Well, in the fullness of time, those years have come nigh upon us. Today we briefly look at the housing market, then the mortgage foreclosure debacle, and then we go into the real problem lurking in the background. It is The Subprime Debacle, Act 2. It is NOT the mortgage foreclosure issue, as serious as that is. I seriously doubt it will be contained, as well. Could the confluence of a bank credit crisis in the US and a sovereign debt banking crisis in Europe lead to another full-blown world banking crisis? The potential is there. This situation wants some serious attention.
This letter is going to print a little longer. But I think it is important that you get a handle on this issue.
Where is the Housing Recovery?
We are going to quickly review a few charts from Gary Shilling's latest letter, where he review the housing market in depth. Bottom line, the housing market has not yet begun to recover, and it is not only going to take longer but the decline in prices may be greater than many have forecast. I wrote three years ago that it could be well into 2011 before we get to a "bottom." That may have been optimistic, given what we will cover in this letter.
First, existing and new single-family home sales continue to slide, in the wake of the tax rebate that ended earlier this year. We have declined back to the down-sloping trend line. If you are a seller, this is not a pretty picture.
The homebuilding industry, which was the source of so many jobs last decade (aka the good old days), is on its back. This country needs a healthy housing construction market to get back to lower unemployment, and until the overhang in the foreclosure market is cleared out, that is unlikely to happen.
Lending is tighter, as is reasonable. Banks actually expect you to have the ability to pay back the mortgage you take out (solid FICO scores) and want reasonable down payments. Only 47% of applicants have the FICO score to get the best mortgage rates.
(Sidebar: Gary writes, "Furthermore, false appraisals rose 50% in 2009 from 2008. The tax credit for first-time homebuyers cost taxpayers about $15 billion, twice the official forecast, in part due to fraud. Over 19,000 tax filers claimed the credit but didn't buy houses, while 74,000 who claimed $500 million in refunds already owned homes." Where are the regulators?)
Shilling thinks prices are likely to fall another 20%. Given what I am writing about in the next section, that is a possibility. There is certainly no demand pressure to push up housing prices.
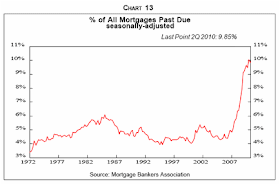
Finally, two charts on foreclosures. Residential mortgages in foreclosure are near all-time highs, close to 1 in 21 of all mortgages, up from 1 in 100 just four years ago. That's got to be bad for your profit models.
Anyone who tells you the housing problem is "bottoming" either has an agenda or simply does not pay attention to the data. I really want to see housing bottom and then turn around and the home builders come back; the nation desperately needs the jobs. But my job is to be realistic. When we see 3-4 months of non-stimulus-induced housing sales growth, then we can start talking about bottoms.
But housing sales are not really the issue. Let's look at the next leg of the problem.
The Foreclosure Mess
OK, in a serendipitous moment, Maine fishing buddy David Kotok sent me this email on the mortgage foreclosure crisis just as I was getting ready to write much the same thing. It is about the best thing I have read on the topic. Saves me some time and you get a better explanation. From Kotok:
"Dear Readers, this text came to me in an email from sources that are in the financial services business and with whom I have a personal relationship. The original text was laced with expletives and I would not use it in the form I received it. Therefore the text below has had some substantial editing in order to remove that language. The intentions of the writer are undisturbed. The writer shall remain anonymous. This text echoes some of the news items we have seen and heard today; however, it can serve as a plain language description of the present foreclosure-suspension mess. There is a lot here. It takes about ten minutes to read it. - David Kotok (www.cumber.com)
"Homeowners can only be foreclosed and evicted from their homes by the person or institution who actually has the loan paper...only the note-holder has legal standing to ask a court to foreclose and evict. Not the mortgage, the note, which is the actual IOU that people sign, promising to pay back the mortgage loan
"Before mortgage-backed securities, most mortgage loans were issued by the local savings & loan. So the note usually didn't go anywhere: it stayed in the offices of the S&L down the street.
"But once mortgage loan securitization happened, things got sloppy...they got sloppy by the very nature of mortgage-backed securities.
"The whole purpose of MBSs was for different investors to have their different risk appetites satiated with different bonds. Some bond customers wanted super-safe bonds with low returns, some others wanted riskier bonds with correspondingly higher rates of return.
"Therefore, as everyone knows, the loans were 'bundled' into REMICs (Real-Estate Mortgage Investment Conduits, a special vehicle designed to hold the loans for tax purposes), and then "sliced & diced"...split up and put into tranches, according to their likelihood of default, their interest rates, and other characteristics.
"This slicing and dicing created 'senior tranches,' where the loans would likely be paid in full, if the past history of mortgage loan statistics was to be believed. And it also created 'junior tranches,' where the loans might well default, again according to past history and statistics. (A whole range of tranches was created, of course, but for the purposes of this discussion we can ignore all those countless other variations.)
"These various tranches were sold to different investors, according to their risk appetite. That's why some of the MBS bonds were rated as safe as Treasury bonds, and others were rated by the ratings agencies as risky as junk bonds.
"But here's the key issue: When an MBS was first created, all the mortgages were pristine...none had defaulted yet, because they were all brand-new loans. Statistically, some would default and some others would be paid back in full...but which ones specifically would default? No one knew, of course. If I toss a coin 1,000 times, statistically, 500 tosses the coin will land heads...but what will the result be of, say, the 723rd toss? No one knows.
"Same with mortgages.
"So in fact, it wasn't that the riskier loans were in junior tranches and the safer ones were in senior tranches: rather, all the loans were in the REMIC, and if and when a mortgage in a given bundle of mortgages defaulted, the junior tranche holders would take the losses first, and the senior tranche holder last.
"But who were the owners of the junior-tranche bond and the senior-tranche bonds? Two different people. Therefore, the mortgage note was not actually signed over to the bond holder. In fact, it couldn't be signed over. Because, again, since no one knew which mortgage would default first, it was impossible to assign a specific mortgage to a specific bond.
"Therefore, how to make sure the safe mortgage loan stayed with the safe MBS tranche, and the risky and/or defaulting mortgage went to the riskier tranche?
"Enter stage right the famed MERS...the Mortgage Electronic Registration System.
"MERS was the repository of these digitized mortgage notes that the banks originated from the actual mortgage loans signed by homebuyers. MERS was jointly owned by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac (yes, those two again ...I know, I know: like the chlamydia and the gonorrhea of the financial world...you cure 'em, but they just keep coming back).
"The purpose of MERS was to help in the securitization process. Basically, MERS directed defaulting mortgages to the appropriate tranches of mortgage bonds. MERS was essentially where the digitized mortgage notes were sliced and diced and rearranged so as to create the mortgage-backed securities. Think of MERS as Dr. Frankenstein's operating table, where the beast got put together.
"However, legally...and this is the important part...MERS didn't hold any mortgage notes: the true owner of the mortgage notes should have been the REMICs.
"But the REMICs didn't own the notes either, because of a fluke of the ratings agencies: the REMICs had to be "bankruptcy remote," in order to get the precious ratings needed to peddle mortgage-backed Securities to institutional investors.
"So somewhere between the REMICs and MERS, the chain of title was broken.
"Now, what does 'broken chain of title' mean? Simple: when a homebuyer signs a mortgage, the key document is the note. As I said before, it's the actual IOU. In order for the mortgage note to be sold or transferred to someone else (and therefore turned into a mortgage-backed security), this document has to be physically endorsed to the next person. All of these signatures on the note are called the 'chain of title.'
"You can endorse the note as many times as you please...but you have to have a clear chain of title right on the actual note: I sold the note to Moe, who sold it to Larry, who sold it to Curly, and all our notarized signatures are actually, physically, on the note, one after the other.
"If for whatever reason any of these signatures is skipped, then the chain of title is said to be broken. Therefore, legally, the mortgage note is no longer valid. That is, the person who took out the mortgage loan to pay for the house no longer owes the loan, because he no longer knows whom to pay.
"To repeat: if the chain of title of the note is broken, then the borrower no longer owes any money on the loan.
"Read that last sentence again, please. Don't worry, I'll wait.
"You read it again? Good: Now you see the can of worms that's opening up.
"The broken chain of title might not have been an issue if there hadn't been an unusual number of foreclosures. Before the housing bubble collapse, the people who defaulted on their mortgages wouldn't have bothered to check to see that the paperwork was in order.
"But as everyone knows, following the housing collapse of 2007-'10-and-counting, there has been a boatload of foreclosures...and foreclosures on a lot of people who weren't sloppy bums who skipped out on their mortgage payments, but smart and cautious people who got squeezed by circumstances.
"These people started contesting their foreclosures and evictions, and so started looking into the chain-of-title issue, and that's when the paperwork became important. So the chain of title became crucial and the botched paperwork became a nontrivial issue.
"Now, the banks had hired 'foreclosure mills'...law firms that specialized in foreclosures...in order to handle the massive volume of foreclosures and evictions that occurred because of the housing crisis. The foreclosure mills, as one would expect, were the first to spot the broken chain of titles.
"Well, what do you know, it turns out that these foreclosure mills might have faked and falsified documentation, so as to fraudulently repair the chain-of-title issue, thereby 'proving' that the banks had judicial standing to foreclose on delinquent mortgages. These foreclosure mills might have even forged the loan note itself...
"Wait, why am I hedging? The foreclosure mills did actually, deliberately, and categorically fake and falsify documents, in order to expedite these foreclosures and evictions. Yves Smith at Naked Capitalism, who has been all over this story, put up a price list for this 'service' from a company called DocX...yes, a price list for forged documents. Talk about your one-stop shopping!
"So in other words, a massive fraud was carried out, with the inevitable innocent bystanders getting caught up in the fraud: the guy who got foreclosed and evicted from his home in Florida, even though he didn't actually have a mortgage, and in fact owned his house free -and clear. The family that was foreclosed and evicted, even though they had a perfect mortgage payment record. Et cetera, depressing et cetera.
"Now, the reason this all came to light is not because too many people were getting screwed by the banks or the government or someone with some power saw what was going on and decided to put a stop to it...that would have been nice, to see a shining knight in armor, riding on a white horse.
"But that's not how America works nowadays.
"No, alarm bells started going off when the title insurance companies started to refuse to insure the titles.
"In every sale, a title insurance company insures that the title is free -and clear ...that the prospective buyer is in fact buying a properly vetted house, with its title issues all in order. Title insurance companies stopped providing their service because...of course...they didn't want to expose themselves to the risk that the chain of title had been broken, and that the bank had illegally foreclosed on the previous owner.
"That's when things started getting interesting: that's when the attorneys general of various states started snooping around and making noises (elections are coming up, after all).
"The fact that Ally Financial (formerly GMAC), JP Morgan Chase, and now Bank of America have suspended foreclosures signals that this is a serious problem...obviously. Banks that size, with that much exposure to foreclosed properties, don't suspend foreclosures just because they're good corporate citizens who want to do the right thing, and who have all their paperwork in strict order...they're halting their foreclosures for a reason.
"The move by the United States Congress last week, to sneak by the Interstate Recognition of Notarizations Act? That was all the banking lobby. They wanted to shove down that law, so that their foreclosure mills' forged and fraudulent documents would not be scrutinized by out-of-state judges. (The spineless cowards in the Senate carried out their master's will by a voice vote...so that there would be no registry of who had voted for it, and therefore no accountability.)
"And President Obama's pocket veto of the measure? He had to veto it...if he'd signed it, there would have been political hell to pay, plus it would have been challenged almost immediately, and likely overturned as unconstitutional in short order. (But he didn't have the gumption to come right out and veto it...he pocket vetoed it.)
"As soon as the White House announced the pocket veto...the very next day!...Bank of America halted all foreclosures, nationwide.
"Why do you think that happened? Because the banks are in trouble...again. Over the same thing as last time...the damned mortgage-backed securities!
"The reason the banks are in the tank again is, if they've been foreclosing on people they didn't have the legal right to foreclose on, then those people have the right to get their houses back. And the people who bought those foreclosed houses from the bank might not actually own the houses they paid for.
"And it won't matter if a particular case...or even most cases...were on the up -and up: It won't matter if most of the foreclosures and evictions were truly due to the homeowner failing to pay his mortgage. The fraud committed by the foreclosure mills casts enough doubt that, now, all foreclosures come into question. Not only that, all mortgages come into question.
"People still haven't figured out what all this means. But I'll tell you: if enough mortgage-paying homeowners realize that they may be able to get out of their mortgage loans and keep their houses, scott-free? That's basically a license to halt payments right now, thank you. That's basically a license to tell the banks to take a hike.
"What are the banks going to do...try to foreclose and then evict you? Show me the paper, Mr. Banker, will be all you need to say.
"This is a major, major crisis. The Lehman bankruptcy could be a spring rain compared to this hurricane. And if this isn't handled right...and handled right quick, in the next couple of weeks at the outside...this crisis could also spell the end of the mortgage business altogether. Of banking altogether. Hell, of civil society. What do you think happens in a country when the citizens realize they don't need to pay their debts?"
(I am not sure who wrote this, but if you want your 15 minutes of fame, I will be glad to credit you next week. - John)
Some Foreclosure Takeaways
Let me add a few thoughts. First, I agree, this is very serious. It has the possibility of seriously hurting the housing market, which as we saw in the first section is already on the ropes. But at the end of the day, there is a cure.
Someone borrowed money for a mortgage. Some entity is cashing a check if that person is paying. That entity should have the title until it is paid off. If someone is not making their mortgage payments, they should be removed from the house and it should be sold to the benefit of the ultimately correct and what everyone thought was the proper title holder.
If you took out a mortgage and now the title is in some doubt because the investment banks and mortgage banks and all the middle guys screwed up (big-time!) because they wanted to save some bucks and make some commissions, you did not win the lottery. That is not America as I know it. You can't pay the mortgage, I am sorry. But you do not get to keep the house. The people who (thought) they bought the mortgage in a fair deal need to end up with that mortgage.
If you pay your mortgage, you get to have the American Dream.
We CANNOT allow this debacle to continue. It will bring the system down. Who will want to buy a mortgage that is in a securitized package with no clear title? Who will get title insurance? Some judge somewhere is going to make a ruling that is going to petrify every title company, and the whole thing grinds to a halt.
Let's be very clear. If we cannot securitize mortgages, there is no mortgage market. We cannot go back to where lenders warehoused the notes. It would take a decade to build that infrastructure. In the meantime, housing prices are devastated. Whatever wealth effect remains from housing gets worse, and the economy rolls over.
This is beyond my pay grade, but there have to be some adults who can make everyone play nice in the sandbox. Ideally, someone in authority at the Treasury, with bipartisan support steps in and says everyone follow these rules, whatever these rules need to be.
I had a very spirited conversation with good friend Barry Ritholtz today (of The Big Picture). Barry runs money but is also a lawyer and has a somewhat different perspective. He thinks we do not need any legislation and there is a legal cure. He says that real trained people (lawyers and paralegals) need to look at each mortgage and figure it out, and that it can get resolved. It is expensive to the banks; but I agree, if it is just dollars I don't care. Fix it.
But that is a maybe. Other people I talk to disagree. Some think we need some regulatory fixes. Some think we will need a legislative cure. But if we need to, there need be no finger pointing, no partisan BS. This needs to get solved.
Someone took out a mortgage. Some entity thinks they are owed money. Fix the damn paper trail so that happens, whether in a legal if time-consuming manner, in a regulatory fix, or with legislation.
Now, that is not to say the people who did this stuff did not commit felonies and such. We can sort that out over time. The longer we wait the worse it will get. Fix the problem and then go round up the bad guys. There are bigger issues in play here. (I know this will be somewhat controversial. Oh well.)
I get the fraud being done here. I am regulated by FINRA, the NFA, various states, the British FSA, and ultimately the SEC. If I did something in my business like the stuff described above, someone would come in and justifiably shut me down, fine me, and ban me from the securities business. Oh, wait. These guys ARE regulated by the above groups.
Finally on this topic, I shake my head when I think that the FDIC is now running several of the banks (think IndyMac) that are part of this foreclosure crisis. These are the guys who are supposed to be preventing something like this. Again, where are the adults?
The Subprime Debacle: Act 2
OK, this letter is already getting too long. I am going to finish it next week, as the next topic needs a lengthy treatment. But I will not leave you hanging. A quick preview.
All those subprime and Alt-A mortgages written in the middle of the last decade? They were packaged and sold in securities. They have had huge losses. But those securities had representations and warranties about what was in them. And guess what, the investment banks may have stretched credibility about those warranties. There is the real probability that the investment banks that sold them are going to have to buy them back. We are talking the potential for multiple hundreds of billions of dollars in losses that will have to be eaten by the large investment banks. We will get into details, but it could create the potential for some banks to have real problems.
And all this coming as European banks are going to have to sort out their own sovereign debt problems. Shades of 2008. I hope I am wrong, but it's all connected.
John Mauldin
John@FrontLineThoughts.com




No comments:
Post a Comment